In the fast-paced world of omnichannel retailing, staying ahead of the competition requires leveraging cutting-edge technologies and insights to create seamless and personalized customer experiences. One such technology that holds immense promise is Generative AI. By combining the power of artificial intelligence with retail insights, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth, customer engagement, and operational efficiency. In this blog, we will explore how the integration of retail insights can enhance Generative AI in omnichannel retailing. We will also delve into some compelling use cases to demonstrate the practical applications and benefits of this approach.
The Role of Retail Insights in Generative AI:
Retail insights encompass a vast amount of data generated throughout the customer journey, including purchasing behavior, preferences, demographics, social media interactions, and more.
These insights provide a deep understanding of customers, market trends, and operational performance.
Combining retail insights with Generative AI enables personalized and contextually relevant experiences.
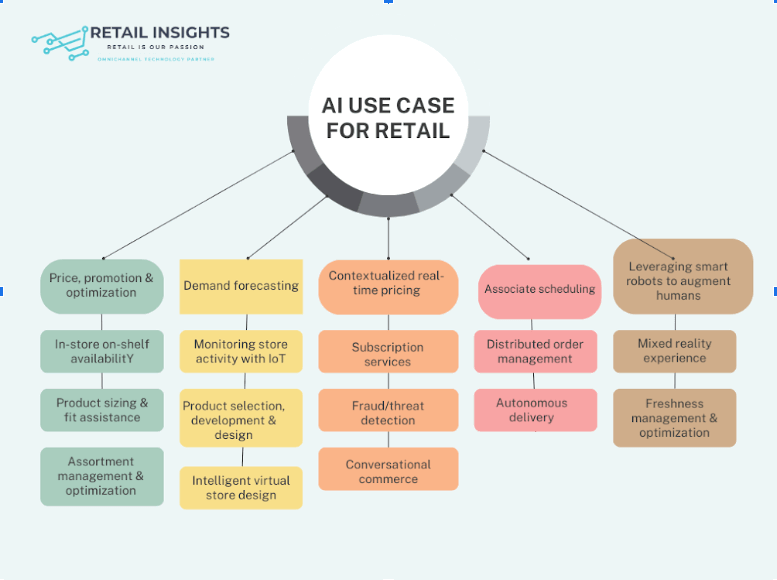
Use Cases for Retail Insights in AI:
Personalized Product Recommendations:
Analyze customer preferences, historical purchase data, and real-time behavior to generate accurate recommendations.
Enhance customer satisfaction, drive conversion rates, and foster brand loyalty.
Dynamic Pricing Optimization:
Leverage retail insights such as competitor pricing, demand patterns, and customer purchasing behavior.
Optimize pricing strategies dynamically, maximize revenue, improve competitiveness, and ensure optimal pricing.
Intelligent Inventory Management:
Use retail insights to forecast demand, optimize stock levels, and automate replenishment processes.
Integrate real-time sales data, supply chain information, and external factors for optimal inventory allocation, reduced stockouts, and lower carrying costs.
Hyper-Personalized Marketing Campaigns:
Combine Generative AI with retail insights to create tailored marketing campaigns.
Leverage demographic data, browsing behavior, purchase history, and customer preferences for increased engagement, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction.
Customer Segmentation and Targeting:
Utilize retail insights to segment customers based on their preferences, behaviors, and demographics. Generative AI can then be used to create targeted marketing campaigns and personalized experiences for each customer segment, improving customer engagement and conversion rates.
Fraud Detection and Prevention:
Leverage retail insights and Generative AI algorithms to identify patterns and anomalies in customer behavior, transaction data, and online activities. This can help in detecting and preventing fraudulent activities, protecting both the business and customers from potential risks.
Demand Forecasting and Supply Chain Optimization:
Combine retail insights with Generative AI to forecast future demand for products based on historical sales data, market trends, and external factors. This enables businesses to optimize their supply chain processes, improve inventory management, and ensure the availability of products when and where they are needed.
Customer Sentiment Analysis:
Analyze customer feedback, reviews, and social media interactions using Generative AI techniques to gain insights into customer sentiment. This can help businesses understand customer perceptions, identify areas for improvement, and tailor their products and services accordingly.
Visual Merchandising and Store Layout Optimization:
By incorporating retail insights, such as customer traffic patterns, product interactions, and sales data, Generative AI can assist in optimizing store layouts and visual merchandising strategies. This ensures that products are strategically placed, improving customer navigation, and enhancing the overall shopping experience.
Predictive Maintenance:
Combine retail insights with AI algorithms to predict maintenance requirements for equipment, machinery, and infrastructure. By analyzing historical performance data, sensor readings, and operational parameters, businesses can proactively schedule maintenance activities, reduce downtime, and improve operational efficiency.
Tools Used in Harnessing Retail Insights for Generative AI:
Data Collection and Integration:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems
Point-of-sale (POS) systems
Social media analytics tools
Data Processing and Analysis:
Big data processing frameworks (e.g., Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark)
Machine learning libraries (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch)
Natural language processing (NLP) tools
Generative AI Model Development:
Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
Variational autoencoders (VAEs)
Deep learning frameworks (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch)
System Integration and Monitoring:
Application programming interfaces (APIs)
Microservices architecture
Monitoring and analytics tools
Conclusion:
The fusion of retail insights and Generative AI presents an incredible opportunity for omnichannel retailers to deliver exceptional customer experiences, drive operational efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth. By incorporating use cases such as personalized product recommendations, dynamic pricing optimization, intelligent inventory management, and hyper-personalized marketing campaigns, businesses can leverage the power of data-driven decision-making. Through the utilization of tools for data collection, processing, Generative AI model development, system integration, and monitoring, retailers can unlock the full potential of retail insights in enhancing Generative AI for omnichannel retailing.